October 25, 2021 Analysis of Canadian provincial data
This summarizes analyses of data from the Canadian provinces with substantial cases. The model includes additional infection cycles to represent the alpha and delta variants of concern. Past vaccination rates are included in the models.
Summary
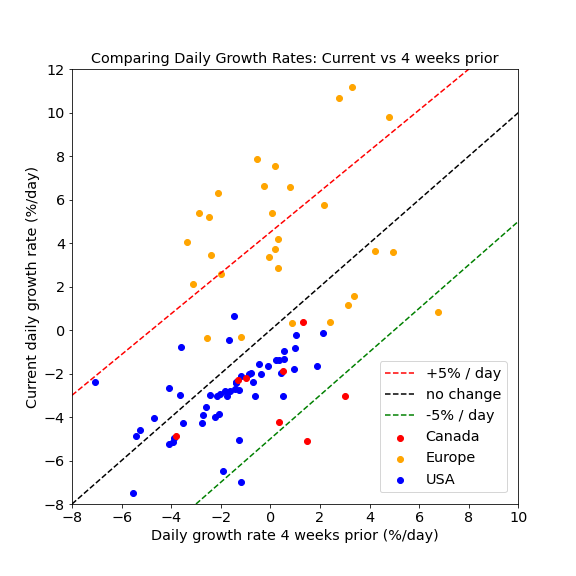
Starting in August, the delta variant produced rapid growth in most provinces, at a rate of 5% or more per day. That growth rate has since subsided significantly, due in part additional health measures.
For all provinces, daily growth rates for cases are currently negative, meaning that infection rates are in decline. Furthermore, the daily growth rates themselves are trending more negative. Some provinces have a growth rate that is 2%/day less than they were 4 weeks ago. That rate of change of the growth rate is consistent with the effect of increasing immunity in the population. Other provinces have recently imposed new measures that have produced a larger reduction in growth rates.
The comparison of growth rates now and 4 weeks ago are shown in the figure below for US states, Canadian provinces, and European nations. The situation in Europe is very concerning, showing an increase in growth rates by 5%/day or more, resulting in rapid growth in the majority of Europe. European studies are posted here.
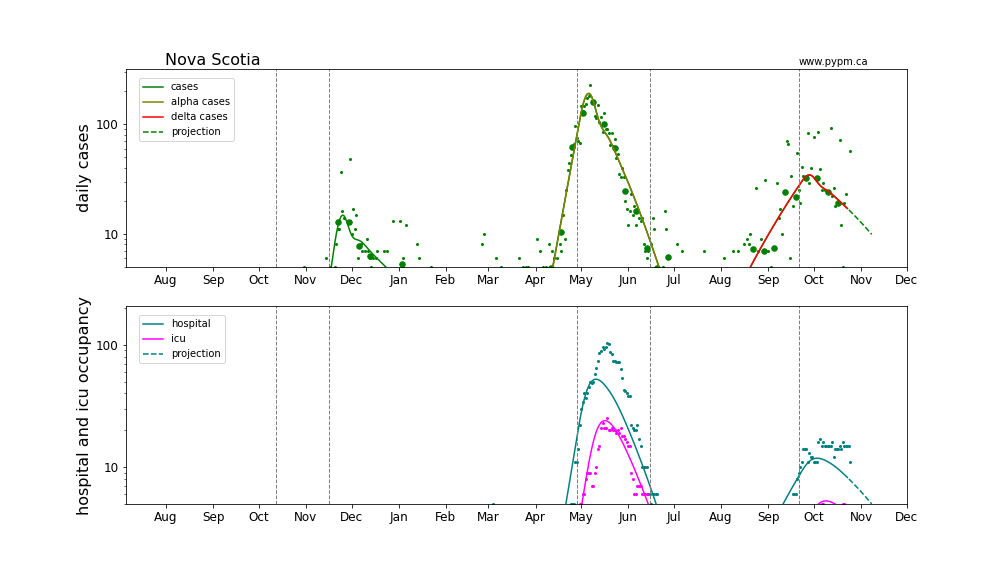
Current fits to data
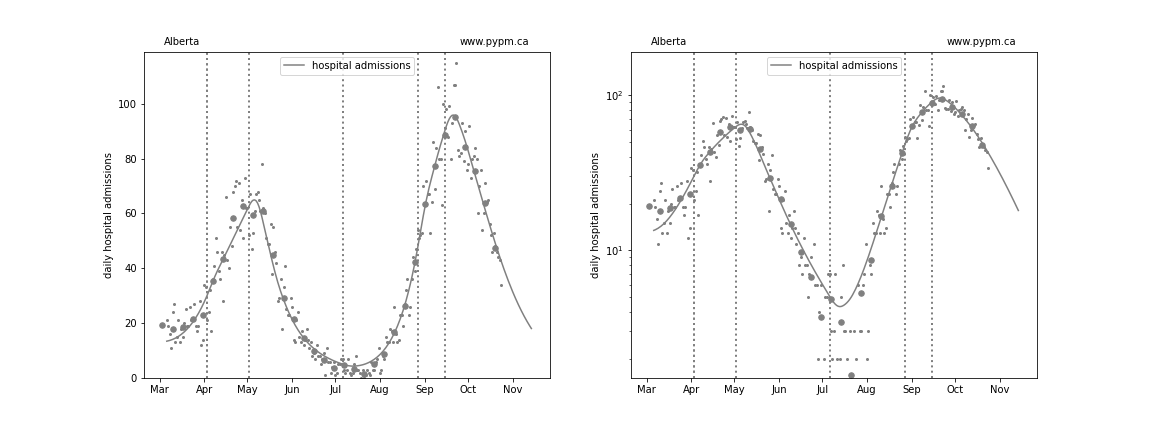
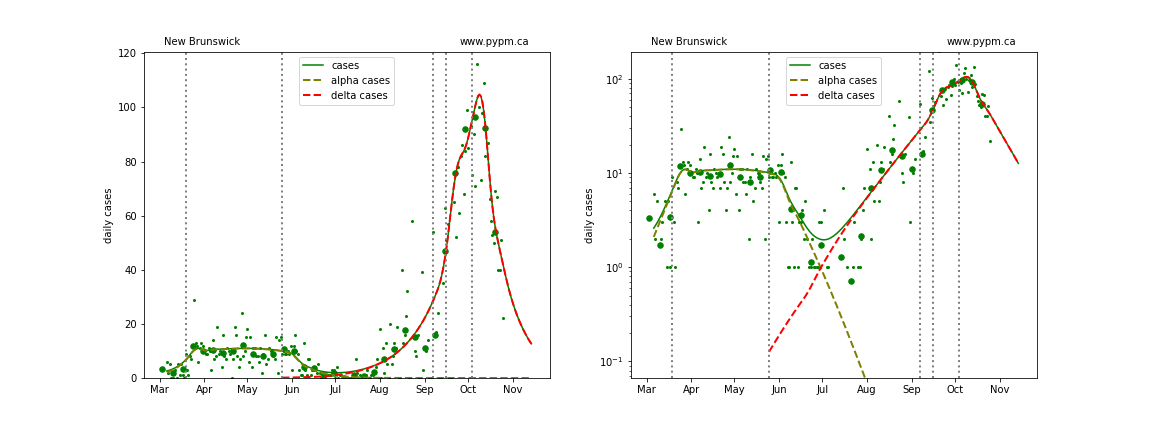
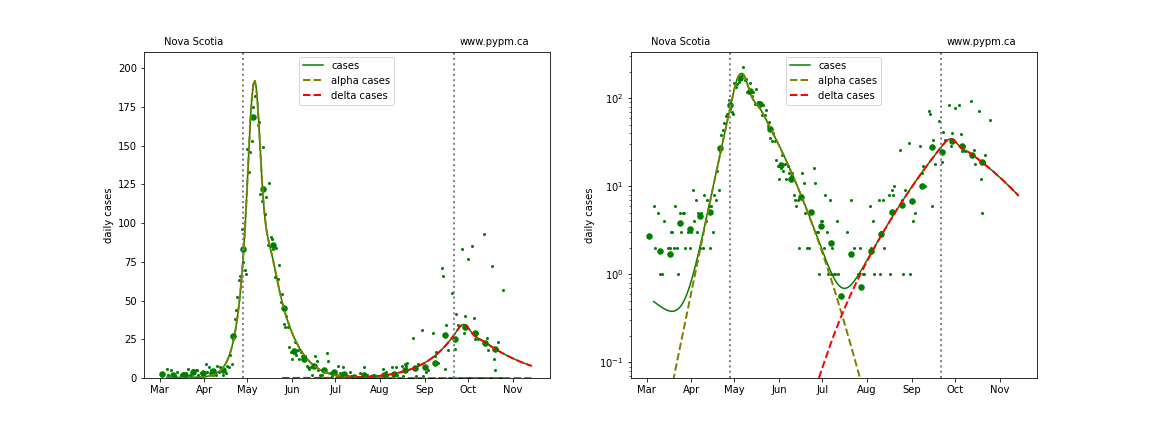
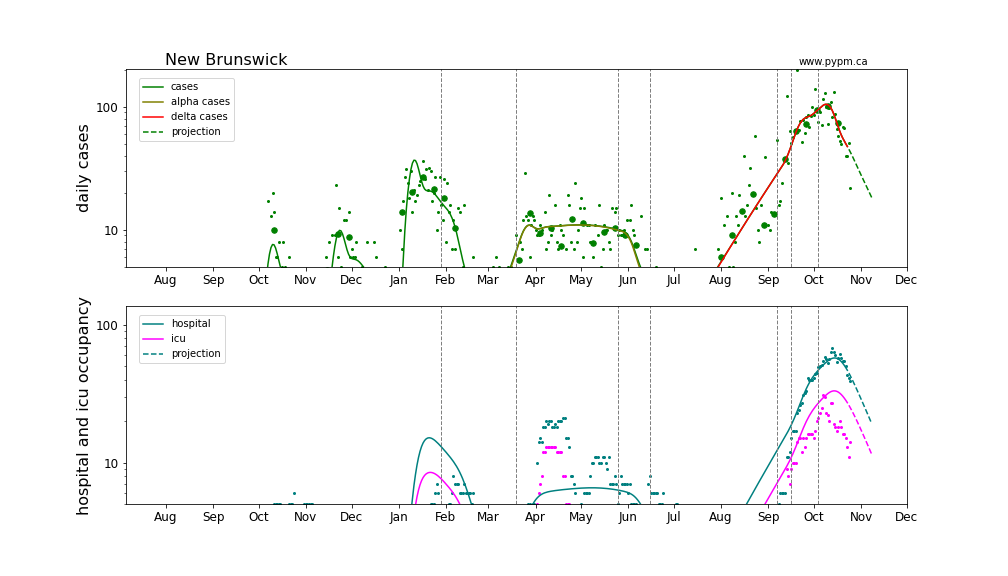
Generally cases are used to define the infection model, since they have the highest statistics and are widely available. Starting August 2021, it appears that testing policy has significantly affected the fraction of infections that are reported as cases. The study establishing that connection is shown in the reports dated October 4 and September 28. For Alberta, after August 1 2021, daily hospital admission data are used in place of cases.
Updated model fits to provincial data are shown below on linear and log-scale:
BC
Detailed BC analyses are reported in the BC analysis page.
Alberta
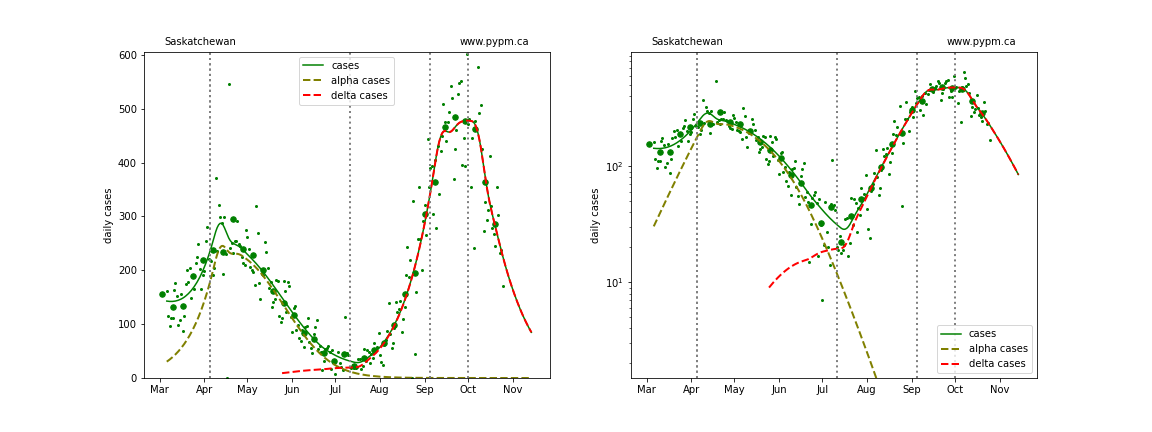
Saskatchewan
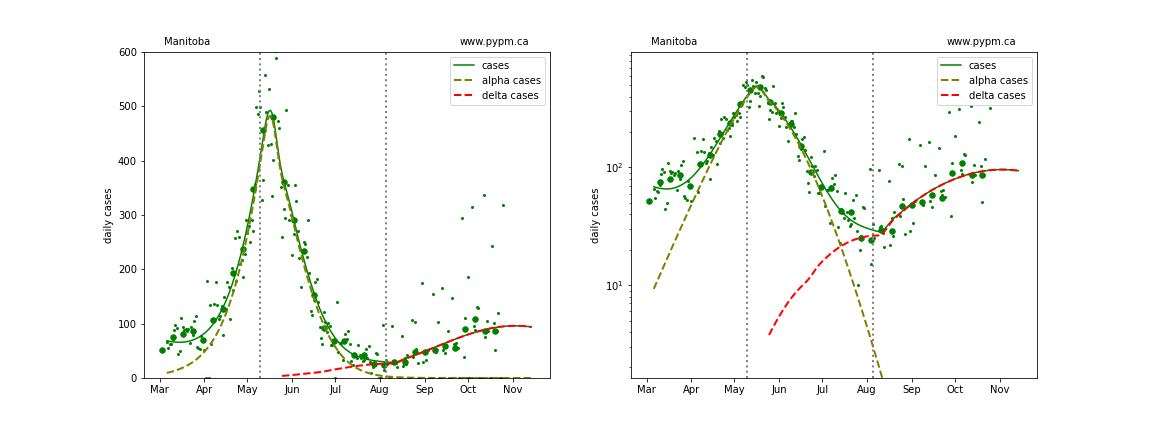
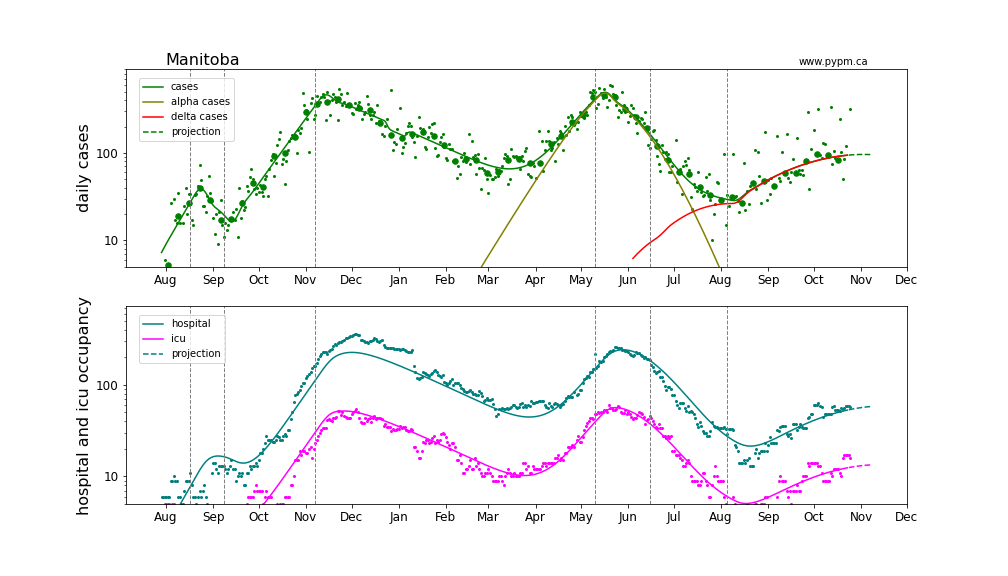
Manitoba
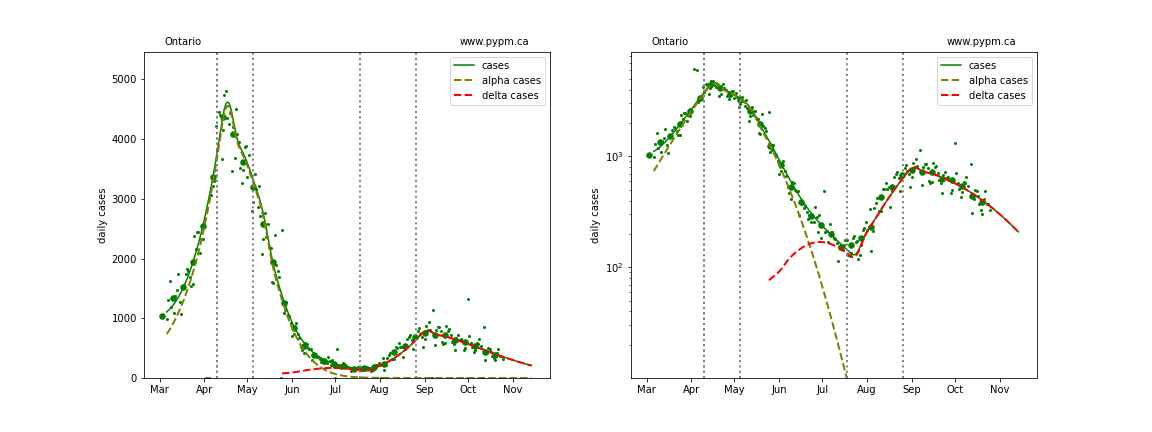
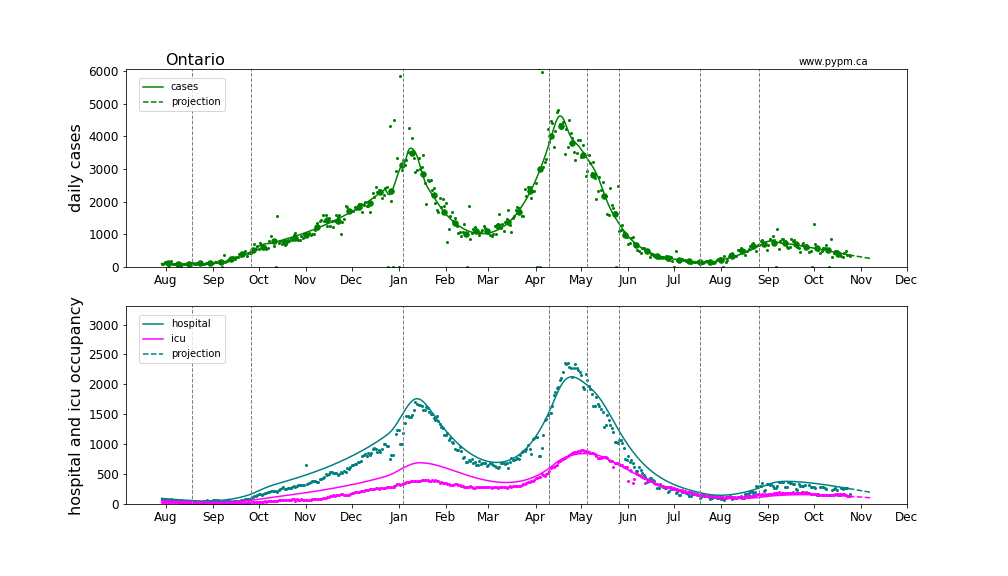
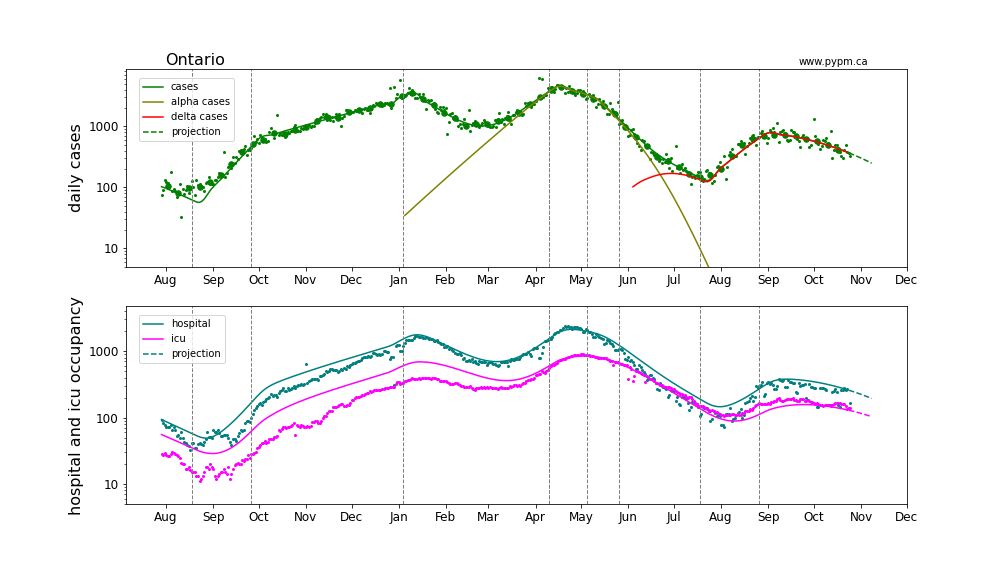
Ontario
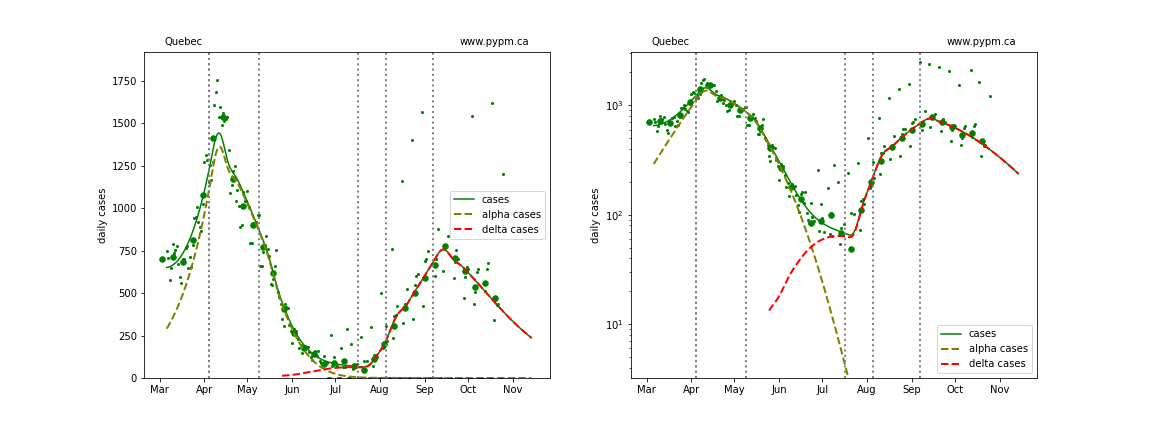
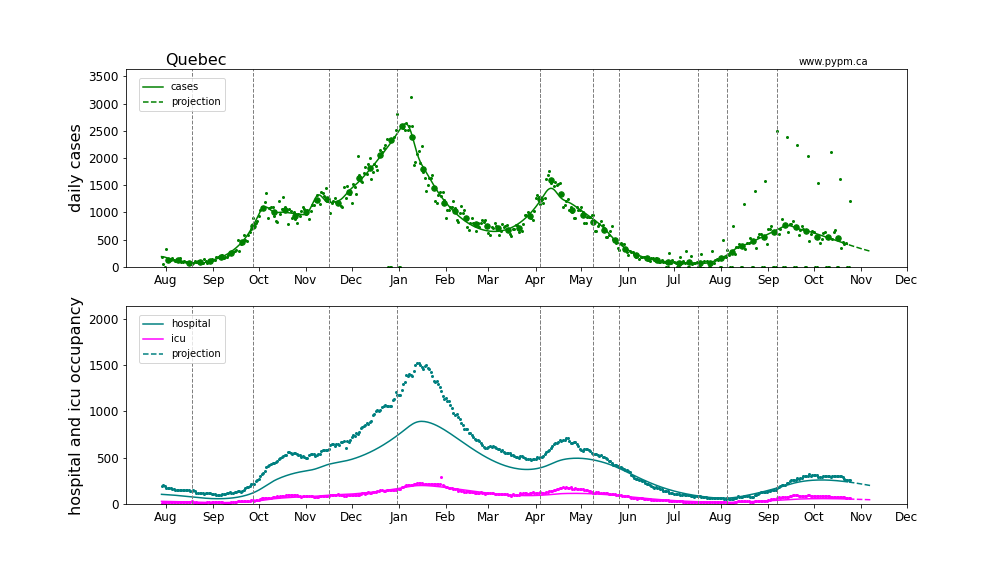
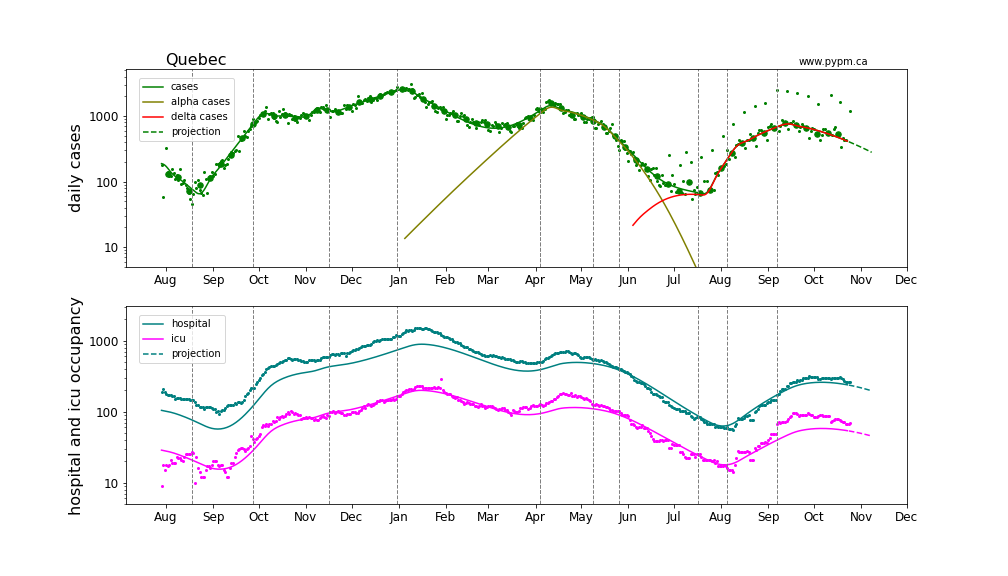
Quebec
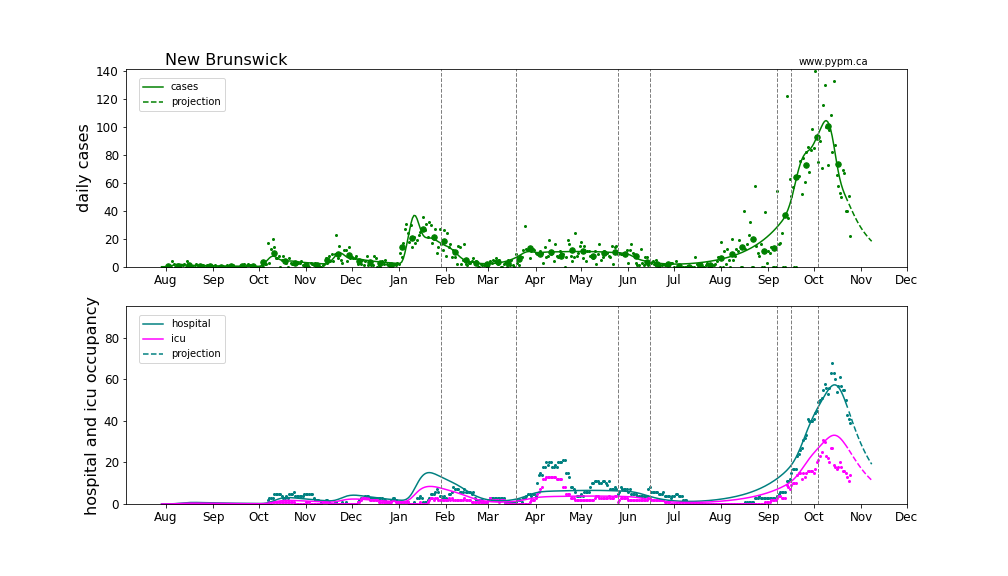
New Brunswick
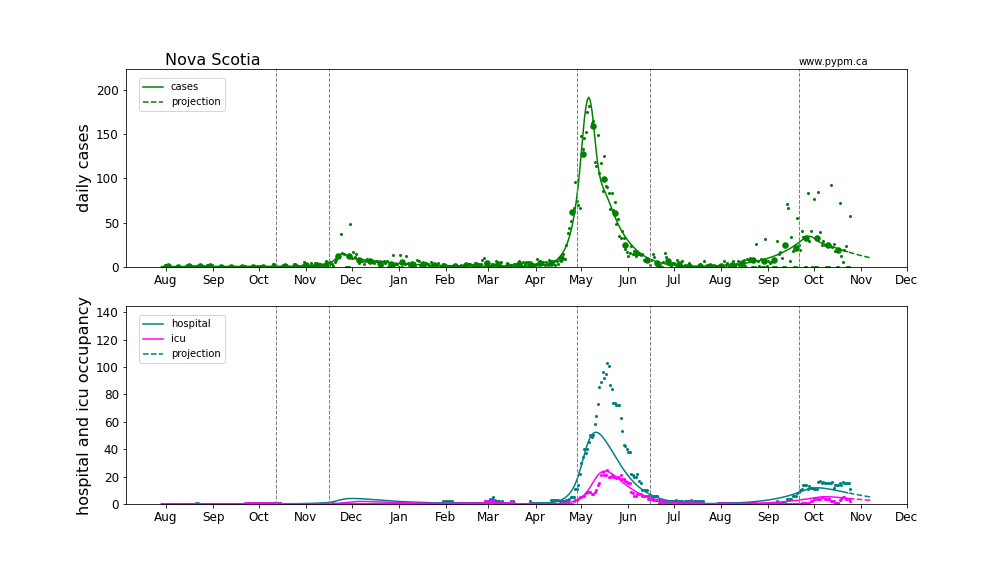
Nova Scotia
Current growth rate
The table below indicates the growth rates (% per day) for each province for recent analyses
| Rpovince | Aug 30 | Sep 7 | Sep 13 | Sep 21 | Sep 28 | Oct 4 | Oct 13 | Oct 25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | +2% | +1% | +1% | 0% | -1% | -1% | -1% | -2% |
| Alberta | +6% | +4% | +2% | +2% | +1% | -7 +/- 3% | -4% | -5% |
| Saskatchewan | +5% | +5% | +4% | +2% | +1% | 0% | -1% | -4% |
| Manitoba | - | - | +2% | +1% | +1% | +1% | +1% | 0% |
| Ontario | +4% | +3% | +1% | 0% | -1% | -1% | -2% | -2% |
| Quebec | +4% | +4% | +2% | +1% | +1% | -2% | -3% | -2% |
| New Brunswick | - | - | - | - | +5% | +5% | +2% | -5% |
| Nova Scotia | - | - | - | - | +5% | +4% | -3% | -3% |
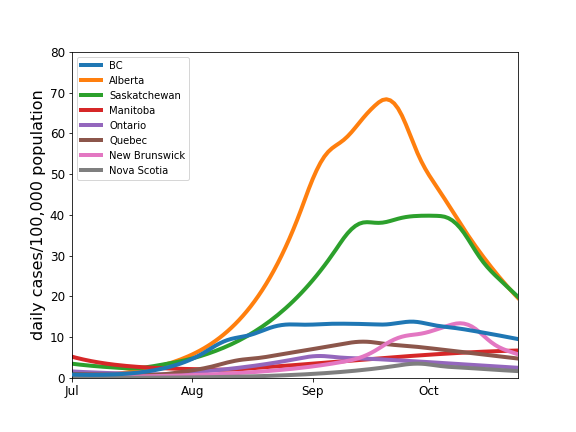
The plot below compares the daily cases as a proportion of population, indicating the serious situations in Alberta and Saskatchewan. The Alberta calculation uses hospital admissions, and the curve corresponds to the expected number of cases had testing not be changed in Alberta in August 2021.
Provincial histories and projections with hospital occupancy
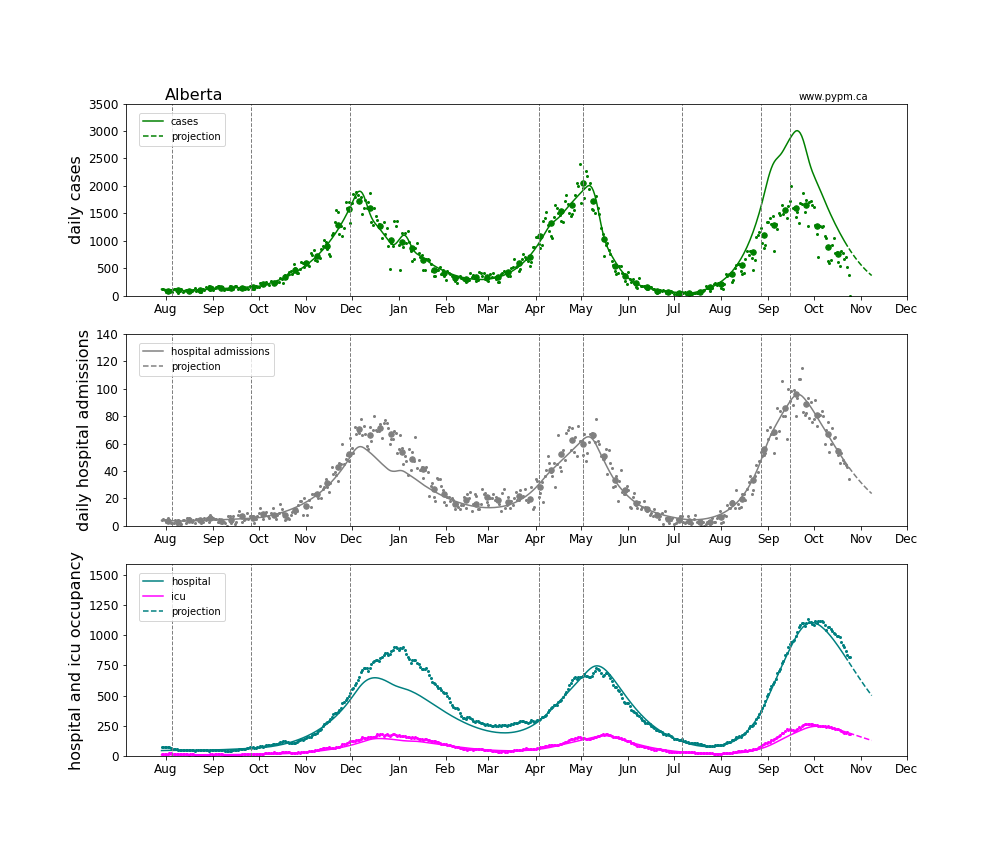
Linear and log scale are shown to see details. Generally, hospitalization is rising in accord with the model projection that assumes the fraction of cases that lead to hospitalization is constant throughout the year. The hospitalization projections for the Atlantic provinces are hampered by low statistics.
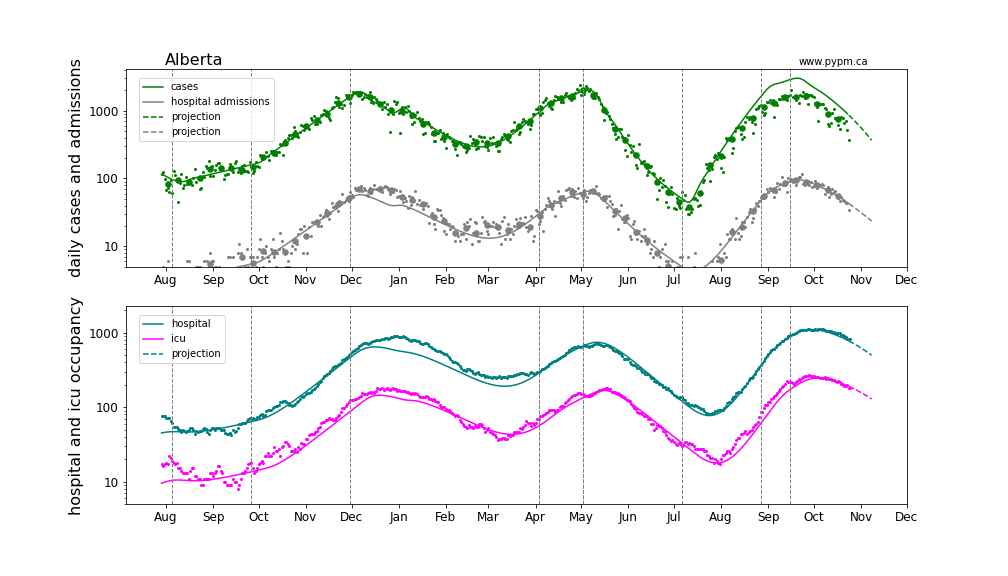
Alberta
The Alberta analysis uses hospital admission data to estimate the growth of infections after August 1, 2021. The case projection exceeds the number of observed cases, with the difference being cases that were missed in Alberta due to changes in testing policy.
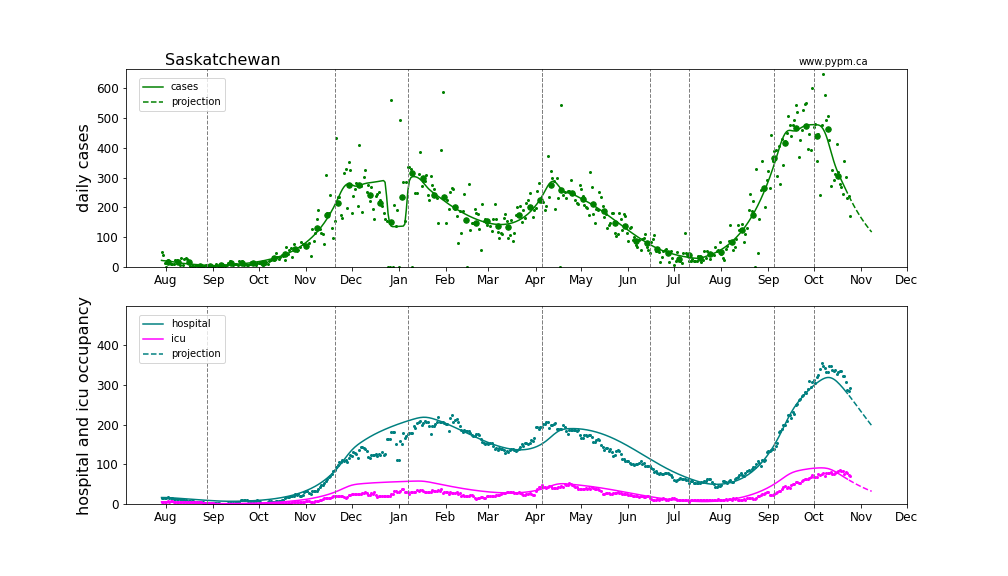
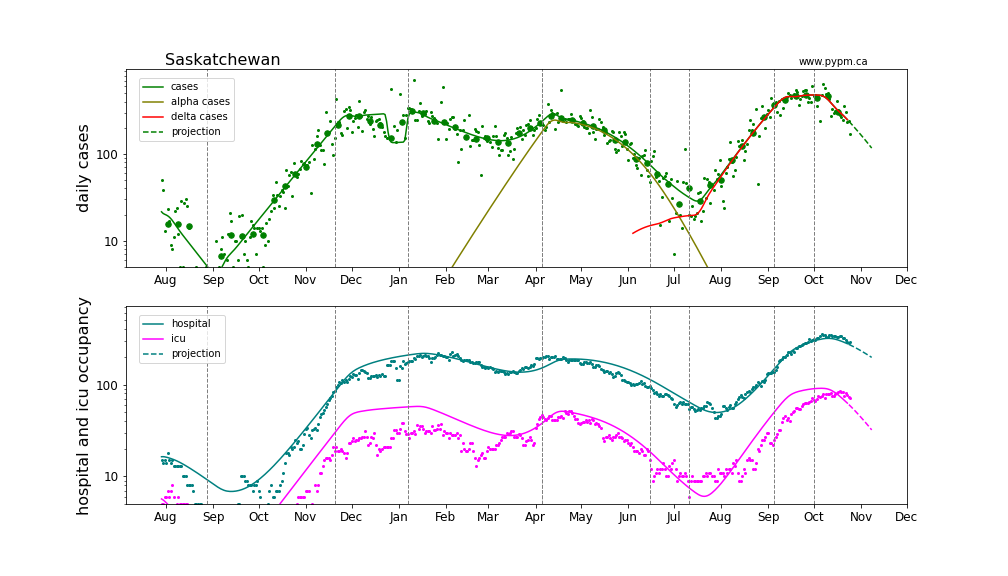
Saskatchewan
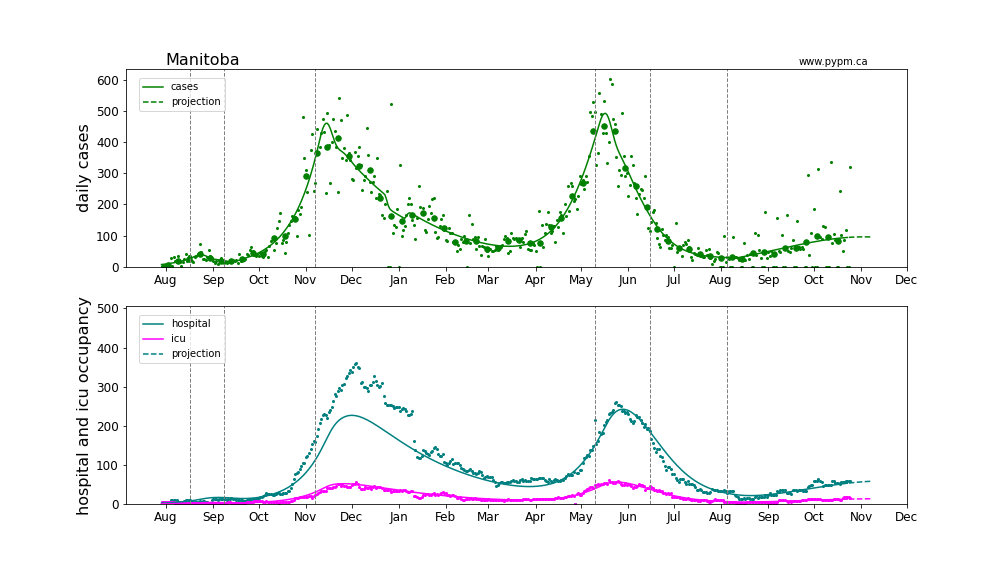
Manitoba
Ontario
Quebec
New Brunswick
Nova Scotia